by Stop Golden Rice! Network and GRAIN | 22 Feb 2018 Seeds
The recent release of Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) approval report of the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) application for a Golden Rice ‘safety stamp’ and trade liability clearance have garnered negative reactions and widespread critique.
The recent release of Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) approval report of the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) application for a Golden Rice ‘safety stamp’ and trade liability clearance have garnered negative reactions and widespread critique.
by ANAFAE, REDSAG, Red de Biodiversidad, Grupo Semillas, Acción Ecológica, Articulación Nacional de Agroecología, Acción por la Biodiversidad and GRAIN | 29 Jan 2018 Seeds | Multimedia
Jointly produced by eight Latin American organisations and edited by Radio Mundo Real, the documentary "Seeds: commons or corporate property?" draws on the experiences and struggles of social movements for the defence of indigenous and native seeds in Ecuador, Brazil, Costa Rica, Mexico, Honduras, Argentina, Colombia, and Guatemala.
Jointly produced by eight Latin American organisations and edited by Radio Mundo Real, the documentary "Seeds: commons or corporate property?" draws on the experiences and struggles of social movements for the defence of indigenous and native seeds in Ecuador, Brazil, Costa Rica, Mexico, Honduras, Argentina, Colombia, and Guatemala.
by IDEF, Eburnie Today, JVE Côte d’Ivoire, GRAIN | 12 Dec 2017 Land
It all started one morning in August 2011 when three village communities in eastern-central Côte d’Ivoire learned that a Belgian corporation called SIAT was about to move onto their land. Not long afterward, an agribusiness firm started putting in a rubber monoculture on 11,000 ha that the communities had neither sold nor ceded and that SIAT was not entitled to exploit.
It all started one morning in August 2011 when three village communities in eastern-central Côte d’Ivoire learned that a Belgian corporation called SIAT was about to move onto their land. Not long afterward, an agribusiness firm started putting in a rubber monoculture on 11,000 ha that the communities had neither sold nor ceded and that SIAT was not entitled to exploit.
by GRAIN | 27 Nov 2017 Corporations | Supermarket Watch
According to different sources, transnational supply chains currently account for 30 to 60 per cent of all global trade, and depend on the work of over 100 million workers globally. On average, companies relying on transnational supply chains only directly hire 6 per cent of the labour force they actually employ. The rest is “outsourced”, often scattered across several countries and amongst thousands of suppliers.
According to different sources, transnational supply chains currently account for 30 to 60 per cent of all global trade, and depend on the work of over 100 million workers globally. On average, companies relying on transnational supply chains only directly hire 6 per cent of the labour force they actually employ. The rest is “outsourced”, often scattered across several countries and amongst thousands of suppliers.
by GRAIN | 20 Nov 2017 Seeds
The autonomy of African states on seed policy is limited by trade deals, such as free trade agreements or investment treaties, signed by States. Certainly, in principle, each country has sovereignty to sign or not sign these agreements. But they are very often forced to conclude them for financial, geopolitical, security or other reasons. GRAIN published a baseline study of these agreements, either signed or in the process of being negotiated, in June 2016 (see “Trade agreements that privatise biodiversity outside the WTO, Annex 1”). Today, what is the situation?
The autonomy of African states on seed policy is limited by trade deals, such as free trade agreements or investment treaties, signed by States. Certainly, in principle, each country has sovereignty to sign or not sign these agreements. But they are very often forced to conclude them for financial, geopolitical, security or other reasons. GRAIN published a baseline study of these agreements, either signed or in the process of being negotiated, in June 2016 (see “Trade agreements that privatise biodiversity outside the WTO, Annex 1”). Today, what is the situation?
by GRAIN, IATP and Heinrich Böll Foundation | 7 Nov 2017 Climate
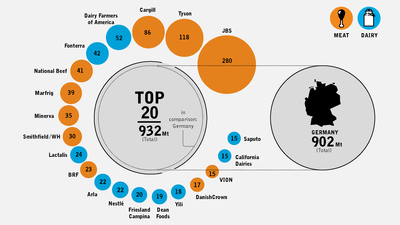
Three meat companies - JBS, Cargill and Tyson - emitted more greenhouse gases last year than all of France and nearly as much as some of the biggest oil companies like Exxon, BP and Shell. Few meat and dairy companies calculate or publish their climate emissions. So for the first time ever, we have estimated corporate emissions from livestock, using the most comprehensive methodology created to date by the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). And before the meat and dairy industries descend upon COP23 to broadcast their “feed the world” narrative, let’s set the story straight: their emissions could lead us to a point of no return.
Three meat companies - JBS, Cargill and Tyson - emitted more greenhouse gases last year than all of France and nearly as much as some of the biggest oil companies like Exxon, BP and Shell. Few meat and dairy companies calculate or publish their climate emissions. So for the first time ever, we have estimated corporate emissions from livestock, using the most comprehensive methodology created to date by the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). And before the meat and dairy industries descend upon COP23 to broadcast their “feed the world” narrative, let’s set the story straight: their emissions could lead us to a point of no return.
by No-REDD Africa, No Vox Togo, Oilwatch Africa and GRAIN | 6 Nov 2017 Climate
Morocco will hand the presidency over to Fiji at the Conference of Parties (COP23) of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change taking place in Bonn, Germany.
Morocco will hand the presidency over to Fiji at the Conference of Parties (COP23) of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change taking place in Bonn, Germany.
by GRAIN | 5 Oct 2017 Corporations |
The new wave of free trade agreements, written by and for corporate interests, provides little or no benefits for workers, communities, or the environment. Provisions being laid in these new trade deals turn most developing countries into sources of cheap and unprotected labour for transnational companies. Labour rights are being redefined in a way that allows transnational companies to impose brutal working conditions. Once these agreements are signed and ratified, the only legal protection that will fully stand is the abolition of slavery. All other labour rights will be disposable at the companies’ discretion under a wide range of circumstances.
The new wave of free trade agreements, written by and for corporate interests, provides little or no benefits for workers, communities, or the environment. Provisions being laid in these new trade deals turn most developing countries into sources of cheap and unprotected labour for transnational companies. Labour rights are being redefined in a way that allows transnational companies to impose brutal working conditions. Once these agreements are signed and ratified, the only legal protection that will fully stand is the abolition of slavery. All other labour rights will be disposable at the companies’ discretion under a wide range of circumstances.
by GRAIN and Ashlesha Khadse | 4 Oct 2017 Corporations
India is being cornered to open up its markets at the ongoing negotiations of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). A free trade agreement between 16 Asian countries, including massive manufacturers like China, RCEP will bring down import duties to zero on goods, both agricultural and industrial, for more than 92 per cent of tariff lines. Being the world’s largest trade agreement, it will impact half of the world’s population including 420 million small family farms that produce 80 per cent of Asia’s food.
India is being cornered to open up its markets at the ongoing negotiations of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). A free trade agreement between 16 Asian countries, including massive manufacturers like China, RCEP will bring down import duties to zero on goods, both agricultural and industrial, for more than 92 per cent of tariff lines. Being the world’s largest trade agreement, it will impact half of the world’s population including 420 million small family farms that produce 80 per cent of Asia’s food.
by Anywaa Survival Organisation and GRAIN | 22 Sep 2017 Media releases | Land
Land activists around the world celebrated the news of the collapse of one of the world’s biggest land grabs: the Indian company Karuturi Global Ltd’s 300,000 hectare farmland deal in Ethiopia. CEO Sai Ramakrishna Karuturi claimed he would bring food security to the horn of Africa while boasting he would soon join the ranks of the world’s biggest food producers.
Land activists around the world celebrated the news of the collapse of one of the world’s biggest land grabs: the Indian company Karuturi Global Ltd’s 300,000 hectare farmland deal in Ethiopia. CEO Sai Ramakrishna Karuturi claimed he would bring food security to the horn of Africa while boasting he would soon join the ranks of the world’s biggest food producers.
by GRAIN | 28 Aug 2017 Corporations | Supermarket Watch
In June 2017, Amazon, the world’s third largest e-commerce company, announced its acquisition over Whole Foods Market for US$ 13.7 billion. Amazon’s move seems to follow the footsteps of Alibaba, the world’s largest e-commerce company that invested US$ 1.25 billion in buying the Chinese online food delivery service Ele.me in late 2015.
In June 2017, Amazon, the world’s third largest e-commerce company, announced its acquisition over Whole Foods Market for US$ 13.7 billion. Amazon’s move seems to follow the footsteps of Alibaba, the world’s largest e-commerce company that invested US$ 1.25 billion in buying the Chinese online food delivery service Ele.me in late 2015.
by GRAIN | 21 Aug 2017 Corporations
Since 2002, African, Caribbean and Pacific (ACP) countries have negotiated a reciprocal free trade agreement known as the Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) with the European Union (EU). While it was marketed as the magic bullet towards the ACP countries’ industrialisation and development, it is in fact an unfair agreement that is anchored in a colonial framework.
Though not highly publicised, the EPA has faced continued opposition from across the ACP countries, not least because of its devastating effect on small scale farmers. The case of some African countries presented here is illustrative of the way communities are fighting to regain control over their resources and protect their markets from the flooding of cheap EU processed foods, along with pesticides and genetically modified organisms.
Since 2002, African, Caribbean and Pacific (ACP) countries have negotiated a reciprocal free trade agreement known as the Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) with the European Union (EU). While it was marketed as the magic bullet towards the ACP countries’ industrialisation and development, it is in fact an unfair agreement that is anchored in a colonial framework.
Though not highly publicised, the EPA has faced continued opposition from across the ACP countries, not least because of its devastating effect on small scale farmers. The case of some African countries presented here is illustrative of the way communities are fighting to regain control over their resources and protect their markets from the flooding of cheap EU processed foods, along with pesticides and genetically modified organisms.
by Stop Golden Rice! Network | 8 Aug 2017 Media releases
Four years after the first militant uprooting of Golden Rice, waves of protest mobilisations stir anew in the Philippines and Bangladesh against its commercialisation, while debate rages on in Indonesia, India and other Asian countries where Golden Rice is planned for commercial release.
Four years after the first militant uprooting of Golden Rice, waves of protest mobilisations stir anew in the Philippines and Bangladesh against its commercialisation, while debate rages on in Indonesia, India and other Asian countries where Golden Rice is planned for commercial release.
by GRAIN | 31 Jul 2017 Corporations |
Hundreds of people gathered in Hyderabad, India, between 22 and 26 July 2017, in opposition to the 19th round of negotiations of the 16-nation Free Trade Agreement (FTA) called the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
Hundreds of people gathered in Hyderabad, India, between 22 and 26 July 2017, in opposition to the 19th round of negotiations of the 16-nation Free Trade Agreement (FTA) called the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
by ILEIA and GRAIN | 21 Jul 2017 Climate
Climate change is a political problem that highlights the need for systemic change to the way food is produced, processed and distributed. From agroecological practices that build resilience, to social movements that resist land grabbing, the articles presented here not only argue for changes to the food system but demonstrate some of the possibilities. A joint editorial in Farming Matters magazine.
Climate change is a political problem that highlights the need for systemic change to the way food is produced, processed and distributed. From agroecological practices that build resilience, to social movements that resist land grabbing, the articles presented here not only argue for changes to the food system but demonstrate some of the possibilities. A joint editorial in Farming Matters magazine.